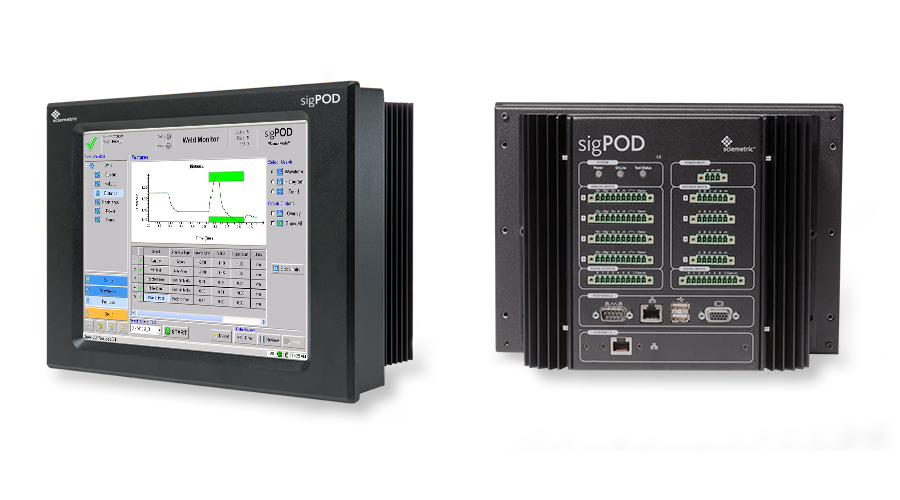
Resistance welding is the process of fastening two metal sub-components together, a very common application across many manufacturing lines. Variations in physical parameters during the weld process, such as the force used during joining, the electrical current and voltage applied to the electrodes and the distance traveled during the melt phase of the process can greatly affect the finished part quality.
Using Sciemetric’s sigPOD welding monitor, manufacturers can effectively measure, monitor, and analyze these parameters during the weld process to capture a broad range of defects, including:
- Inadequate or excessive heating
- Poor bonding due to low energy exposure, presence of foreign materials, or material voids
- Deformation of the part due to excessive force
- Misalignment of probes
- Burned materials due to high energy exposure
- Poor or improperly sized weld ball
- Expulsions (when overheating, poor alignment, or electrode shape causes metal to burst out of the weld zone)
- Deteriorating electrode conditions due to oxidation or change in the gap width
- And more
Sciemetric’s sigPOD weld monitoring system provides full visibility of the process variables and visualizes the data for a clear, accurate view into your weld process and product quality. The sigPOD weld analyzer system offers real-time monitoring and analysis, enabling you to catch defects before they move further down the line and become more difficult and costly to fix, resulting in inefficiencies, scraped parts, and reduction in throughput.
TALK TO AN ENGINEER ABOUT HOW SIGPOD COULD EASILY INTEGRATE INTO YOUR LINE
The Most Accurate Weld Defect Detection Using Sciemetric’s PSV™ Technology
The Sciemetric sigPOD process analyzer system offers extensive measurement, data capture, and waveform processing, equipped with Sciemetric’s unique PSV™ (process signature verification) technology, making it the most accurate spot weld tester. Using digital process signature analysis and process signature verification, manufacturers have access to a clear, visual representation of everything that happened through every millisecond of their weld process.
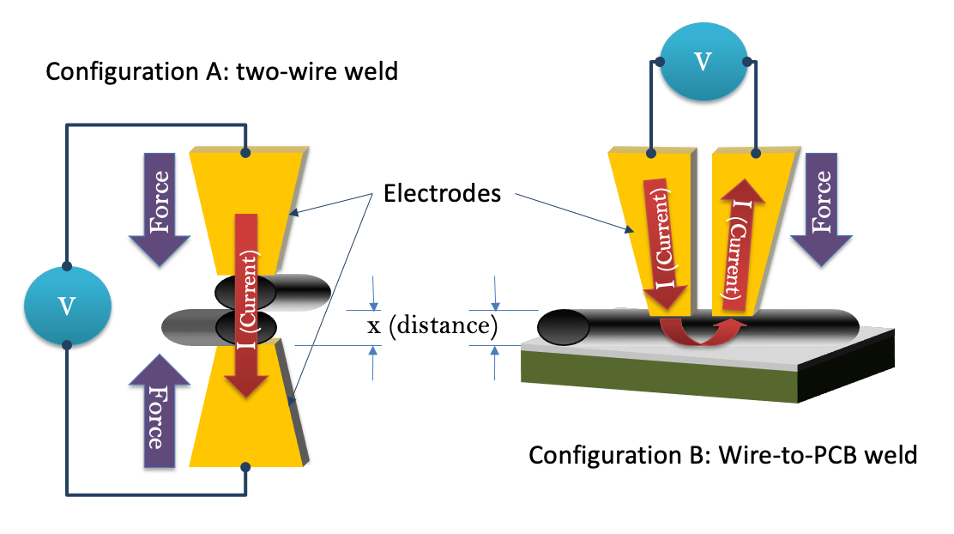
During the weld process, sigPOD weld monitoring equipment is setup to monitor four physical parameters during the weld process: force, current, voltage, and distance. This information is then processed into waveforms, or digital process signatures, for analysis. The sigPOD configures six waveforms to analyze the quality of your weld process: current, voltage, distance, resistance, power, and force. Each of these waveforms can be analyzed and compared to identify specific defects from your weld processes, as follows:
| Waveform | Examples of Defects Detected |
|---|---|
| Current |
|
| Voltage |
|
| Distance |
|
| Resistance |
|
| Power |
|
| Force |
|
How it Works:
For each of these waveforms, sigPOD measures and records hundreds of datapoints, which makeup the unique process signatures (see below example of a waveform monitoring a weld operation).
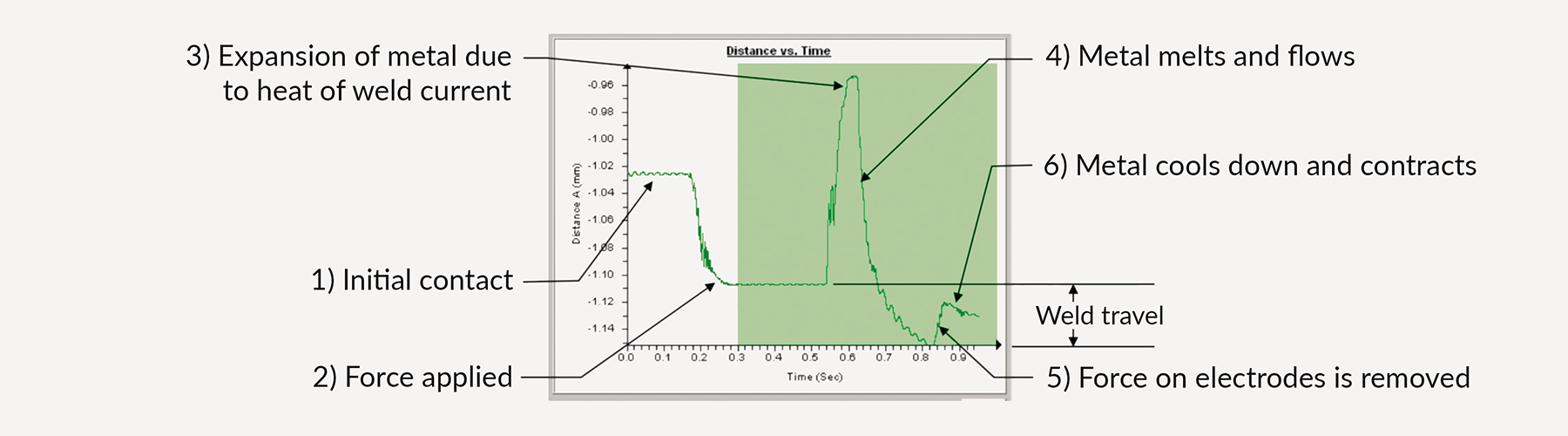
The baseline signature profile of an acceptable weld vs. a failed part/process makes it easy to establish a range of acceptable deviation. This acceptable limit is set in the system and when it is breached, the system will identify the process as a “fail”. This allows you to detect defects in real time before the part moves on to the next station, or even further down the line where the faulty part is more difficult and costly to fix. This software also allows plant engineers to understand where and why the defects occurred, making it easier to prevent issues in the future.
By analyzing and collecting more data points than is typical in conventional test systems, PSV™ provides the most accurate weld monitoring software for reliable and repeatable measurement of manufacturing processes.
Waveform Example: Spotting Weld Expulsion Defect using sigPOD’s PSV™
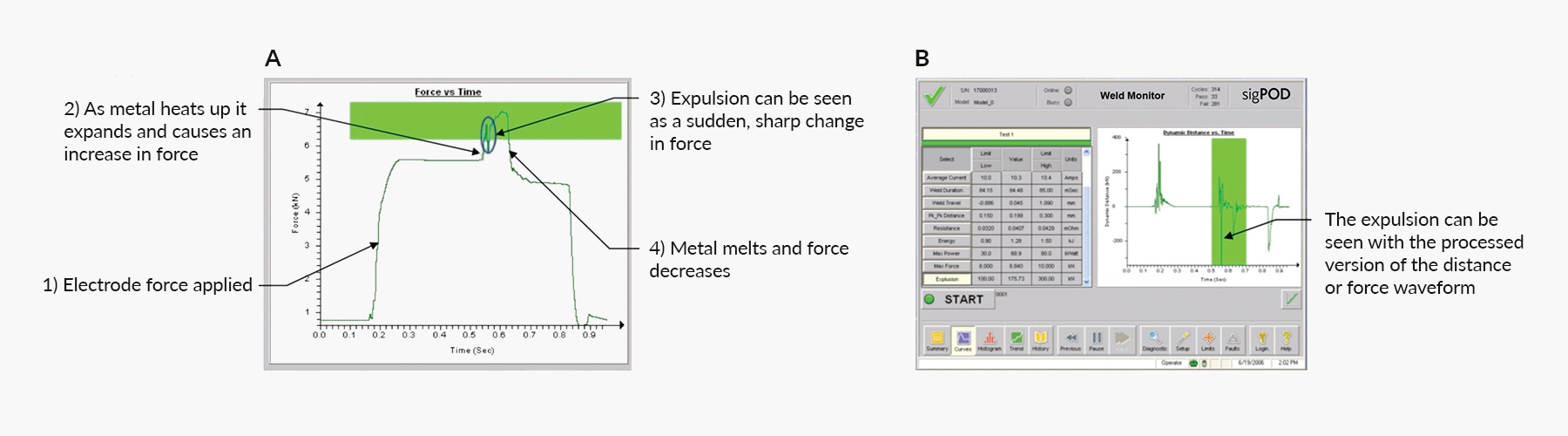
The above waveforms were used to identify a weld expulsion event, which is when molten material spreads beyond the weld zone, which indicates a loss of bonding material and can result in a weak weld joint. The sudden, sharp change in force seen in the force vs. time signature (a) was the first indication of a problem, further confirmed by the characteristic spikes in the processed version of the distance or force waveform (b).
TALK TO AN ENGINEER ABOUT SIGPOD
sigPOD Makes Test Setup Easy
Weld checkers don’t need to be complicated to install. sigPOD comes equipped with simple-to-install application templates for the most common processes on your line, including spot weld monitoring. Simply install the application template, optimize parameters and settings for the specific resistance welder and the sub-components being welded, and you’re ready to test!
Typical Weld Challenges
There are many challenges when it comes to ensuring a quality weld process. Several parameters, including force, current, distance, and voltage must be monitored and controlled for the weld manufacturing process to be effective and reliable. Common challenges include:

- Many Different Materials
- Steels (100’s of types)
- Tungsten, Magnesium, Aluminum, Titanium, etc.
- Homogeneity
- Metallurgic properties, resistance, thickness, configuration, and coatings
- Electrodes & Apparatus
- Shape, plating, current density
- Wear and degradation
- Mechanics
- Force and movement profile
- The physical weld force that is applied
- Weld Control
- Open vs. closed loop
- Welding energy used to generate heat
- The amount of time that the energy is applied
Sciemetric’s sigPOD weld monitoring system enables you to set up the proper controls necessary to catch problems resulting from the above challenges. This allows you to identify issues before they make it further down the line, which results in further cost and reduction in throughput.
TALK TO AN ENGINEER ABOUT PROBLEMS WITH YOUR WELD PROCESS
How Sciemetric’s sigPOD Catches Common Weld Problems
Identifying Weld Expulsion, Common Cause of Weak Welds & Defects
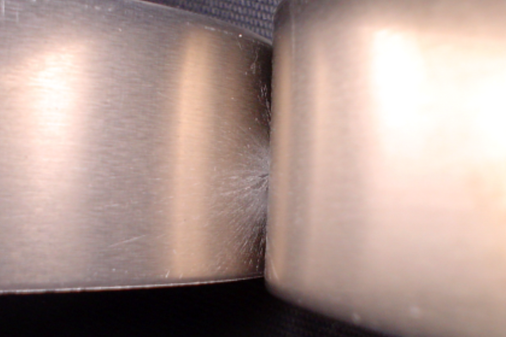
A common quality issue at the weld station on a production line is expulsion – an unwanted ejection of molten material beyond the weld zone that can result in a weak weld joint. Learn how expulsions are caused and how to detect them with sigPOD monitoring and analytics.
Replacing Destructive Pull Tests with Resistance Weld Monitoring
Resistance welding is commonly used in medical device manufacturing, where the integrity of the bonding joint is often critical to the safety of a patient and long-term reliability of the device. Learn how Sciemetric’s sigPOD allowed medical manufacturers to eliminate part auditing using destructive pull tests, boosting accuracy, efficiency, and throughput.
Monitor & Analyze Quality Across Multiple Stations or Processes using sigPOD
Sciemetric’s sigPOD data system can also be connected to QualityWorX, a centralized data management, storage, and archiving system for all of your manufacturing process data. QualityWorX enables networked resistance weld monitoring that allows you to connect your weld stations together for better analysis, and can even be added to other upstream or downstream processes, like leak test or function test.
Connecting different critical-to-quality tests across your line offers the most accurate root cause analysis, with the ability to connect the dots between problems found down the line. Being able to quickly identify the cause of quality problems on your line saves you line downtime and costly scraps and gives you all the information you need to fix the root cause and prevent further similar defects from happening again in the future. A connected manufacturing data and analytics system also enables continuous improvement, constantly monitoring and finding ways to improve and boost efficiency across your processes.

See How Sciemetric’s Connected Data Analytics Enabled Reliable Weld Quality Assurance for Medical Manufacturer
Sciemetric worked with a medical manufacturer that was using destructive pull tests to identify defective assemblies. However, they found that pull-tests for welds on the production line were costly and provided no guarantee that defective assemblies wouldn’t slip through.
After applying Sciemetric’s sigPOD system for weld defect detection and analysis, the manufacturer was able to eliminate destructive pull-testing and guarantee that every weld on every unit, whether it is a pacemaker or another medical device, was robust and reliable.